Subgroup structure of groups of order 8: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
| [[cyclic group:Z8]] || 1 || 3 || 1 || 1 || 0 || 4 | | [[cyclic group:Z8]] || 1 || 3 || 1 || 1 || 0 || 4 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[direct product of Z4 and Z2]] || 2 || 2 || | | [[direct product of Z4 and Z2]] || 2 || 2 || 2 || 1 || 1 || 6 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[dihedral group:D8]] || 3 || 4 || 2 || 1 || 1 || 6 | | [[dihedral group:D8]] || 3 || 4 || 2 || 1 || 1 || 6 | ||
Revision as of 21:32, 29 June 2011
This article gives specific information, namely, subgroup structure, about a family of groups, namely: groups of order 8.
View subgroup structure of group families | View subgroup structure of groups of a particular order |View other specific information about groups of order 8
The list
| Group | Second part of GAP ID | Subgroup structure page | Lattice of subgroups picture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclic group:Z8 | 1 | subgroup structure of cyclic group:Z8 | |
| Direct product of Z4 and Z2 | 2 | subgroup structure of direct product of Z4 and Z2 | |
| Dihedral group:D8 | 3 | subgroup structure of dihedral group:D8 | 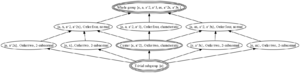
|
| Quaternion group | 4 | subgroup structure of quaternion group | 
|
| Elementary abelian group:E8 | 5 | subgroup structure of elementary abelian group:E8 |
Subgroup/quotient relationships
Subgroup relationships
Quotient relationships
Numerical information on counts of subgroups by isomorphism type
FACTS TO CHECK AGAINST FOR SUBGROUP STRUCTURE: (group of prime power order)
Lagrange's theorem (order of subgroup times index of subgroup equals order of whole group, so all subgroups have prime power orders)|order of quotient group divides order of group (and equals index of corresponding normal subgroup, so all quotients have prime power orders)
prime power order implies not centerless | prime power order implies nilpotent | prime power order implies center is normality-large
size of conjugacy class of subgroups divides index of center
congruence condition on number of subgroups of given prime power order: The total number of subgroups of any fixed prime power order is congruent to 1 mod the prime.
Number of subgroups per isomorphism type
The number in each column is the number of subgroups in the given group of that isomorphism type:
| Group | Second part of GAP ID | Hall-Senior number | cyclic group:Z2 | cyclic group:Z4 | Klein four-group | Total (row sum + 2, for trivial group and whole group) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cyclic group:Z8 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| direct product of Z4 and Z2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 8 |
| dihedral group:D8 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 10 |
| quaternion group | 4 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 6 |
| elementary abelian group:E8 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 16 |
Number of conjugacy classes of subgroups per isomorphism type
The number in each column is the number of conjugacy classes of subgroups in the given group of that isomorphism type:
| Group | Second part of GAP ID | Hall-Senior number | cyclic group:Z2 | cyclic group:Z4 | Klein four-group | Total (row sum + 2, for trivial group and whole group) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cyclic group:Z8 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| direct product of Z4 and Z2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 8 |
| dihedral group:D8 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| quaternion group | 4 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 6 |
| elementary abelian group:E8 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 16 |
Number of normal subgroups per isomorphism type
| Group | Second part of GAP ID | Hall-Senior number | cyclic group:Z2 | cyclic group:Z4 | Klein four-group | Total (row sum + 2, for trivial group and whole group) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cyclic group:Z8 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| direct product of Z4 and Z2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 8 |
| dihedral group:D8 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 6 |
| quaternion group | 4 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 6 |
| elementary abelian group:E8 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 16 |
Number of automorphism classes of subgroups per isomorphism type
The number in each column is the number of automorphism classes of subgroups in the given group of that isomorphism type:
| Group | Second part of GAP ID | Hall-Senior number | cyclic group:Z2 | cyclic group:Z4 | Klein four-group | Total (row sum + 2, for trivial group and whole group) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cyclic group:Z8 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| direct product of Z4 and Z2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| dihedral group:D8 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| quaternion group | 4 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| elementary abelian group:E8 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 |
Numerical information on counts of subgroups by order
Number of subgroups of various kinds per order
| Group | Second part of GAP ID | Hall-Senior number | Subgroups of order 2 | Normal subgroups of order 2 | Subgroups of order 4 | Normal subgroups of order 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cyclic group:Z8 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| direct product of Z4 and Z2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| dihedral group:D8 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| quaternion group | 4 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| elementary abelian group:E8 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
Possibilities for maximal subgroups
| Collection of isomorphism classes of maximal subgroups | Groups |
|---|---|
| cyclic group:Z4 only | cyclic group:Z8, quaternion group |
| Klein four-group only | elementary abelian group:E8 |
| cyclic group:Z4 and Klein four-group | direct product of Z4 and Z2, dihedral group:D8 |

